Abstract
We present new constraints on the relationship between galaxies and their host dark matter halos, measured from the location of the peak of the stellar-to-halo mass ratio (SHMR), up to the most massive galaxy clusters at redshift
and over a volume of nearly 0.1~Gpc
. We use a unique combination of deep observations in the CFHTLenS/VIPERS field from the near-UV to the near-IR, supplemented by
secure spectroscopic redshifts, analysing galaxy clustering, galaxy-galaxy lensing and the stellar mass function. We interpret our measurements within the halo occupation distribution (HOD) framework, separating the contributions from central and satellite galaxies. We find that the SHMR for the central galaxies peaks at
with an amplitude of
, which decreases to
for massive halos (
). Compared to central galaxies only, the total SHMR (including satellites) is boosted by a factor 10 in the high-mass regime (cluster-size halos), a result consistent with cluster analyses from the literature based on fully independent methods. After properly accounting for differences in modelling, we have compared our results with a large number of results from the literature up to
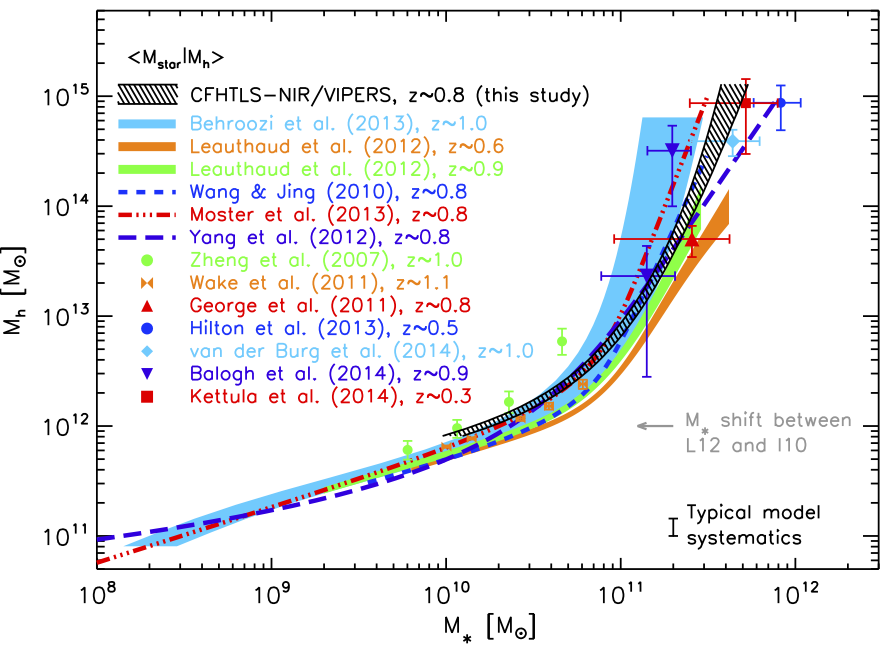
: we find good general agreement, independently of the method used, within the typical stellar-mass systematic errors at low to intermediate mass (
) and the statistical errors above. We have also compared our SHMR results to semi-analytic simulations and found that the SHMR is tilted compared to our measurements in such a way that they over- (under-) predict star formation efficiency in central (satellite) galaxies.