Abstract
Aims. The primordial power spectrum describes the initial perturbations that seeded the large-scale structure we observe today. It provides an indirect probe of inflation or other structure-formation mechanisms. In this letter, we recover the primordial power spectrum from the Planck PR1 dataset, using our recently published algorithm PRISM.
Methods. PRISM is a sparsity-based inversion method, that aims at recovering features in the primordial power spectrum from the empirical power spectrum of the cosmic microwave background (CMB). This ill-posed inverse problem is regularised using a sparsity prior on features in the primordial power spectrum in a wavelet dictionary. Although this non-parametric method does not assume a strong prior on the shape of the primordial power spectrum, it is able to recover both its general shape and localised features. As a results, this approach presents a reliable way of detecting deviations from the currently favoured scale-invariant spectrum.
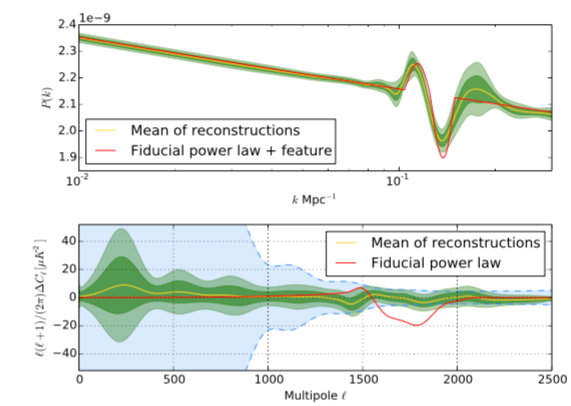
Results. We applied PRISM to 100 simulated Planck data to investigate its performance on Planck-like data. We then applied PRISM to the Planck PR1 power spectrum to recover the primordial power spectrum. We also tested the algorithm’s ability to recover a small localised feature at k ∼ 0.125 Mpc−1, which caused a large dip at l ∼ 1800 in the angular power spectrum.
Conclusions. We find no significant departures from the fiducial Planck PR1 near scale-invariant primordial power spectrum with As = 2.215 × 10−9 and ns = 0.9624.